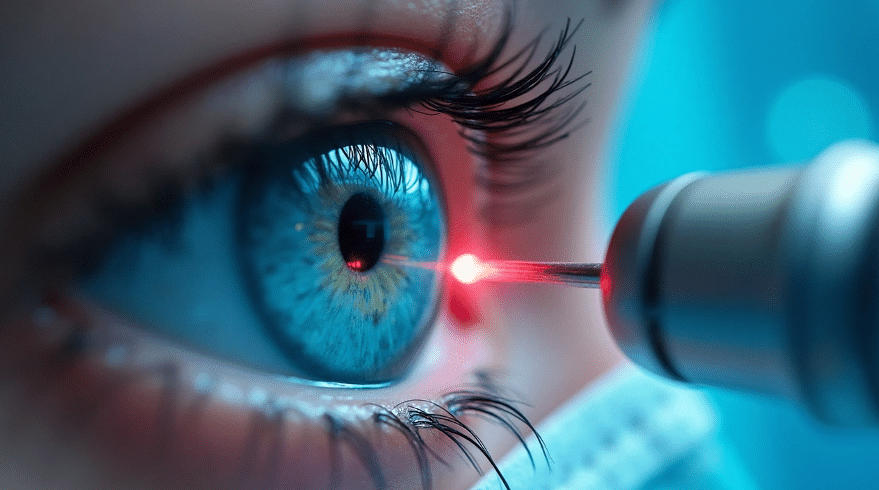
LASIK vs PRK vs SMILE: Which Laser Surgery Fits You Best?
In-depth guide to laser eye surgery covering methods, costs, benefits, recovery, and risks. Explains LASIK, PRK, and SMILE in detail, offering practical advice for candidates seeking lasting vision correction.
In an era where technology is rewriting the boundaries of healthcare, laser eye surgery has become one of the most life-changing medical innovations of the 21st century. For millions of people worldwide, it has offered freedom from glasses, confidence in daily life, and a permanent improvement in how the world is seen.
But what exactly happens during laser eye surgery? How safe is it? And what should be considered before undergoing the procedure? This guide explores all major aspects of laser vision correction — from techniques and costs to long-term results and recovery.
1. How Laser Eye Surgery Works
The core of laser eye surgery lies in reshaping the cornea — the clear, dome-shaped surface that bends light entering the eye. When the cornea is misshapen, light rays don’t focus properly on the retina, leading to nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism.
Laser eye surgery uses highly precise laser technology to correct this. By carefully removing microscopic layers of corneal tissue, surgeons adjust its curvature so that light refocuses perfectly. The result? Sharper, natural vision — without external lenses.
Most procedures are painless, take less than 30 minutes, and allow patients to return home the same day. Vision improvement is often noticeable within a few hours, with full results within several days.
2. Main Types of Laser Eye Surgery
There are three dominant methods used worldwide:
LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis)
The most common and widely known. A thin flap is created on the corneal surface using a femtosecond laser. The underlying tissue is reshaped with an excimer laser and the flap is repositioned. Pros: Fast recovery, minimal pain, stable results within 24 hours. Best for: Patients with moderate myopia or hyperopia and stable prescriptions.
PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy)
One of the earliest techniques, still popular today. The surface layer (epithelium) is removed, and the cornea is reshaped directly. The epithelium naturally regenerates during healing. Pros: Ideal for thin corneas or active individuals. Cons: Slightly longer recovery, with mild discomfort for a few days.
SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction)
The newest generation in laser correction. A femtosecond laser creates a tiny lens-shaped piece of tissue (lenticule), which is extracted through a small incision — no flap needed. Pros: Less invasive, lower risk of dry eyes, quick healing. Best for: Mild to moderate nearsightedness.
3. Cost of Laser Eye Surgery
In North America and Europe, the cost varies depending on technology, clinic reputation, and surgeon expertise.
Prices usually include consultation, surgery, and initial aftercare, though advanced laser systems or follow-ups can increase total expenses. Some clinics offer financing plans to make it more affordable.
4. Benefits That Go Beyond Vision
Laser eye surgery isn’t just about sharper sight — it changes daily living:
- Freedom from glasses or contacts
- Improved comfort in sports, travel, and work
- Increased self-confidence
- Cost savings in the long term — no more replacement lenses or prescriptions
For many, it’s not simply a medical upgrade — it’s a lifestyle transformation.
5. Who Is the Right Candidate?
Not everyone qualifies for laser eye surgery. Generally suitable candidates include:
- Age 21–45 (with stable vision prescription for at least one year)
- No major eye diseases (glaucoma, cataracts, etc.)
- Sufficient corneal thickness
- Good general health
Pregnant or breastfeeding women, and those with autoimmune diseases, are usually advised to wait.
6. The Procedure: What to Expect
Before surgery, patients undergo a detailed eye scan and mapping. On the day of surgery:
- Eye-numbing drops are applied.
- A laser reshapes the cornea in seconds.
- No stitches are needed — the eye naturally heals.
Most people notice a dramatic difference by the next morning. Mild dryness or glare can occur temporarily.
7. Post-Surgery Care and Recovery
Proper aftercare ensures long-term success:
- Avoid rubbing eyes for at least a week.
- Use prescribed lubricating drops regularly.
- Protect eyes from UV light with sunglasses.
- Attend all scheduled follow-up visits.
Within one month, vision usually stabilizes completely. Statistically, over 95% of patients achieve 20/25 vision or better.
8. Potential Risks
While laser eye surgery is considered safe, minor risks exist:
- Dry eyes during recovery
- Halos or night glare
- Undercorrection or overcorrection (rare)
Choosing a certified, experienced ophthalmologist greatly reduces these risks.
9. Long-Term Outlook
Laser eye surgery is designed for permanent correction, though natural aging can still cause presbyopia (difficulty focusing up close) later in life. Many enjoy decades of clear vision without additional treatment.
In recent years, advanced re-treatment options have made fine adjustments even easier, keeping eyesight sharp for the long term.
10. The Emotional Impact
For countless patients, laser eye surgery brings more than physical clarity — it delivers emotional freedom. The first time seeing clearly after waking up, swimming, or reading without glasses often feels like rediscovering the world.
Conclusion
Laser eye surgery stands as a symbol of how technology can improve human life. It’s not only about perfect vision — it’s about the confidence and simplicity that come with it. For those considering the procedure, consulting a qualified surgeon and understanding the available options is the best step toward a clearer, freer future.